How to Manage Foot Wounds at Home: Essential Tips
Introduction
Foot wounds, if not managed properly, can quickly worsen, leading to infections or other complications. With the right approach to home care, minor injuries can be treated effectively and healing can progress smoothly. For professional wound care solutions, explore our Acute and Chronic Wound Care Services. This guide provides essential foot wound care tips to help you manage minor wounds at home and recognize when professional help is necessary.
Proper Cleaning and Dressing Techniques
One of the most important steps in treating foot wounds at home is proper cleaning and dressing. Gently cleanse the wound with a mild antiseptic or saline solution to remove dirt and bacteria, reducing the risk of infection. Our Advanced Wound Healing Techniques provide specialized treatments for faster and safer recovery.. After cleaning, pat the area dry and apply a sterile dressing or bandage to protect the wound and promote faster healing. Choose breathable, non-stick dressings to avoid further irritation. Regularly change the dressing and monitor for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge. Proper foot wound care not only aids recovery but also prevents complications, ensuring optimal foot health.
1. Clean the Wound
Rinse the wound gently with clean, lukewarm water to flush out dirt, debris, and harmful bacteria. Use a mild soap that is free from harsh chemicals to cleanse the surrounding area without causing irritation. Avoid using harsh antiseptics, such as hydrogen peroxide, which can damage healthy tissue and slow the healing process. For deeper wounds, consult a healthcare provider to ensure proper cleaning. Effective wound cleansing minimizes the risk of infection and promotes faster, more effective healing.
2. Apply an Antibacterial Ointment
After thoroughly cleaning the wound, apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment or cream to create a protective barrier against harmful bacteria and prevent infection. Choose ointments that are proven to support wound healing while reducing inflammation. Ensure the ointment covers the wound evenly without over-application, which can hinder breathability. Using antibacterial ointments as part of a wound care routine supports healthy tissue regrowth and lowers the risk of complications like infections.
3. Cover with a Sterile Dressing
Protect the wound by covering it with a breathable, sterile bandage or dressing designed for optimal healing. Change the dressing daily or whenever it becomes wet, soiled, or loose to maintain a clean environment. Keeping the wound covered prevents contamination from dirt, bacteria, or environmental factors while maintaining a moist environment that aids in cell regeneration. Select dressings that adhere gently to the skin and promote quicker healing with reduced scarring. Regular dressing changes are critical for keeping the wound clean and minimizing the risk of infection.
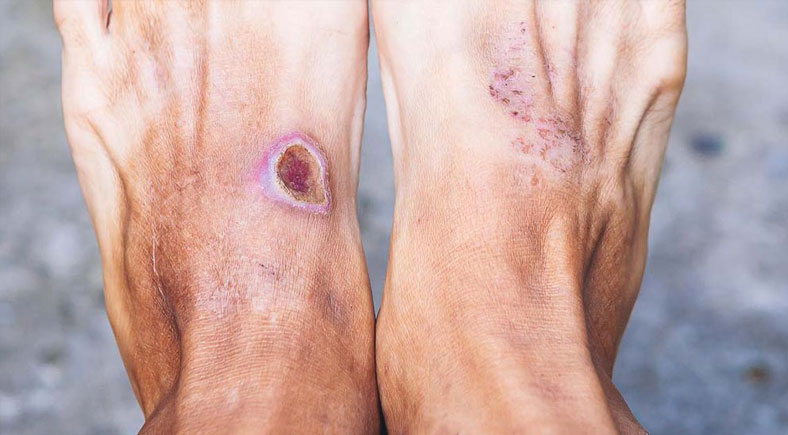
4. Identifying Signs of Infection
Monitoring a foot wound for signs of infection is vital for timely intervention and effective management. If you suspect an infection, consult our Diabetic Ulcer Treatment Services for expert wound care in Chicago. Recognizing symptoms early can prevent complications and support faster recovery. Pay close attention to any changes in the wound or surrounding area, as infections can escalate quickly. Awareness of these key signs ensures you take prompt action and seek medical care if necessary.
5. Redness and Swelling
If the area around the wound becomes red, swollen, or inflamed, it may indicate that an infection is developing. These symptoms often signify the body’s immune response to harmful bacteria. Persistent redness or swelling that spreads beyond the wound’s edges is particularly concerning and should be closely monitored. Addressing redness and swelling early can prevent the infection from worsening and causing more serious complications like cellulitis or abscesses.
6. Pain or Tenderness
A noticeable increase in pain or tenderness around the wound can be an early warning sign of infection. While some discomfort is normal during healing, sharp or escalating pain may suggest the presence of bacteria or tissue damage. If pain persists despite proper wound care, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional to rule out underlying issues like deeper infections or tissue necrosis.
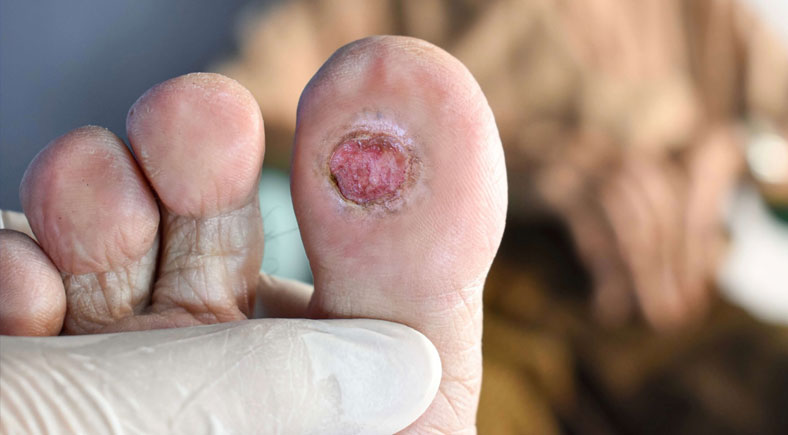
7. Pus or Discharge
The presence of yellow, green, or foul-smelling discharge from the wound is a clear indication of infection. Pus often forms as a result of the body fighting off bacteria and should not be ignored. Proper cleaning and dressing are essential to manage discharge, but if it continues or worsens, medical attention is necessary. Discharge combined with swelling and redness could indicate advanced infection requiring antibiotics or further intervention.
8. Fever or Warmth Around the Area
A fever or warm sensation around the wound site may signal a more severe infection that requires immediate medical care. Warmth indicates increased blood flow to the area due to inflammation, while fever is a systemic response to infection. These symptoms can be signs of a spreading infection, such as sepsis, and should not be overlooked. Seek medical advice promptly to prevent further complications.
When to Seek Professional Help
While some minor foot wounds can be managed at home, knowing when to seek professional care is critical for preventing complications. If your wound is deep, infected, or not healing, our Surgical Wound Care Services offer specialized treatments to ensure proper recovery. Promptly recognizing the need for medical attention can help avoid serious issues, such as infections or long-term damage. Below are the key situations where professional care becomes essential.
1. Deep or Large Wounds
If the wound is deep, excessively large, gaping, or bleeding heavily, consult a doctor immediately. Such wounds may require stitches, specialized dressings, or other interventions to prevent excessive blood loss or infection. Deep wounds can also involve damage to underlying tissues, muscles, or nerves, which only a healthcare professional can assess and treat effectively. Immediate care reduces the risk of complications like delayed healing or severe infections.
2. No Improvement After a Few Days
If the wound does not show signs of healing, such as reduced redness, swelling, or closure, or if it appears to worsen over time, seek medical advice. Persistent wounds could indicate underlying issues such as poor circulation, infection, or inadequate care. A healthcare provider can evaluate the wound and may recommend advanced treatments like antibiotics, debridement, or wound care therapy to promote faster and safer healing.
3. Underlying Health Conditions
Individuals with diabetes, peripheral artery disease, or poor circulation should seek professional care for even minor wounds to prevent complications such as infections, ulcers, or gangrene. These conditions impair the body’s ability to heal properly and require specialized monitoring to avoid severe outcomes. Healthcare professionals can provide customized wound care plans, ensuring that the wound is managed effectively and complications are avoided.
Conclusion
By following these home wound care practices, you can manage foot wounds at home effectively, promote faster healing, and reduce the risk of complications. If you’re dealing with a non-healing wound, Schedule a Consultation with our experts today to receive personalized care. Proper cleaning, dressing, and monitoring of wounds are essential steps in ensuring optimal care. However, it’s equally important to recognize when professional intervention is needed, especially for deeper wounds, signs of infection, or if you have underlying health conditions like diabetes or poor circulation. Timely medical attention can prevent long-term issues, such as chronic wounds or severe infections, which may require advanced treatments. Stay vigilant, prioritize consistent wound care, and consult a healthcare provider when necessary to ensure safe and effective healing. Taking these steps will help maintain overall foot health and prevent complications that could impact mobility or quality of life.