The Importance of Regular Foot Exams for People with Diabetes
Introduction
For individuals living with diabetes, regular foot exams are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Diabetes can damage nerves and blood vessels, leading to numbness, tingling, and poor circulation in the feet. If left unchecked, these complications can result in severe consequences, including diabetic foot ulcers, infections, and even amputations.
Risks of Skipping Foot Exams
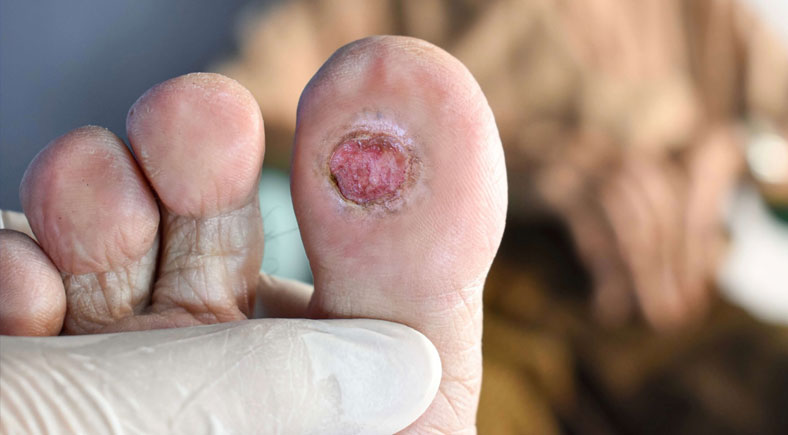
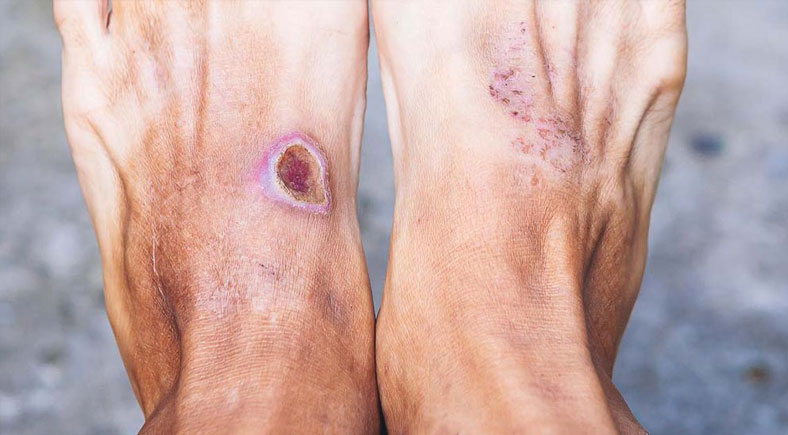
Skipping regular foot exams can have severe consequences for individuals, particularly those with diabetes. Neglecting foot health can have devastating consequences for diabetics. Diabetic foot ulcers, for example, can develop quickly and not be noticeable due to numbness or loss of sensation. If left untreated, these ulcers can become infected, leading to serious health complications. Learn more about effective wound healing techniques to prevent long-term damage. Neglecting foot health can lead to the development of foot ulcers, which can quickly become infected and potentially life-threatening. If these ulcers can progress to gangrene, requiring amputation of the affected limb. In severe cases, amputations may be necessary. Regular foot exams can help identify potential problems early, reducing the risk of severe consequences. Furthermore, nerve damage caused by diabetes can lead to loss of sensation, making it difficult to detect foot injuries or infections, emphasizing the importance of regular foot exams to prevent these devastating complications.
What to Expect During a Regular Foot Exams for Diabetes
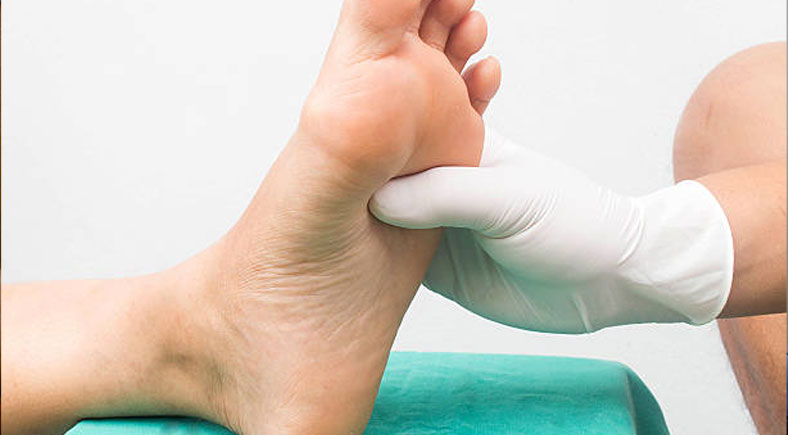
During a foot exam, a healthcare professional will visually inspect your feet for any signs of injury, infection, or abnormality. A typical foot exam for diabetics involves a thorough inspection of the feet, including the toes, nails, and skin. For specialized treatment, consider scheduling an appointment with our podiatry and chronic wound specialists for personalized foot care solutions. The examiner will check for signs of nerve damage, poor circulation, and other potential problems.
This may include:
- Visual inspection for cuts, cracks, or other openings in the skin
- Checking for sensation and reflexes
- Examining the feet for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or warmth
- Checking the nails for signs of fungal infections
The healthcare professional will also check the nails for signs of fungal infections. They may use a monofilament test to assess nerve sensitivity.
How Often Should Diabetics Have Foot Exams?
The frequency of foot exams for diabetics depends on individual risk factors. The American Diabetes Association recommends the following:
1. Low-risk patient
Annual foot exams. Individuals with diabetes who are considered low-risk for foot complications should undergo a comprehensive foot exam at least once a year. This annual exam helps identify potential issues before they become severe.
2. Moderate-risk patients
Foot exams every 3 to 6 months; patients with diabetes who are classified as moderate-risk for foot complications require more frequent exams. These individuals should undergo a thorough foot exam every 3 to 6 months to monitor their foot health and address any emerging issues promptly.
3. High-risk patients
Foot exams every 1 to 3 months; individuals with diabetes who are deemed high-risk for foot complications require regular and frequent exams. These patients should undergo a comprehensive foot exam every 1 to 3 months to closely monitor their foot health and prevent severe complications.
Conclusion
Regular foot exams are crucial for diabetics to maintain ongoing foot health and prevent severe complications. By scheduling regular foot exams, individuals with diabetes can:
- Identify potential problems early.
- Reduce the risk of foot ulcers and infections.
- Prevent amputations.
- Maintain overall health and well-being.
Don’t neglect your foot health; schedule a visit with a specialist in diabetic ulcer treatment today.