Diabetic Foot Ulcer Dressing Guidelines: A Complete Care Guide for Chicago Residents
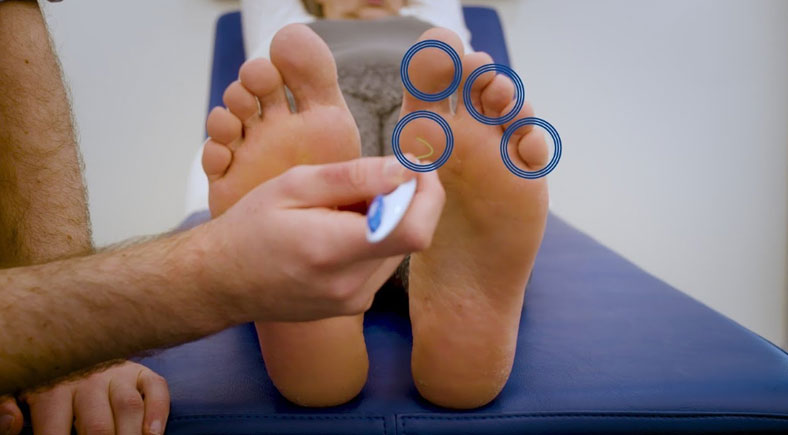
Diabetic foot ulcers are one of the most common complications for people with diabetes, and they can lead to severe issues if not properly managed. When dealing with diabetic foot ulcers, the right dressing is crucial for promoting healing and preventing infection. In this article, we’ll walk you through the essential diabetic foot ulcer dressing guidelines, offering practical advice tailored to residents in Chicago.
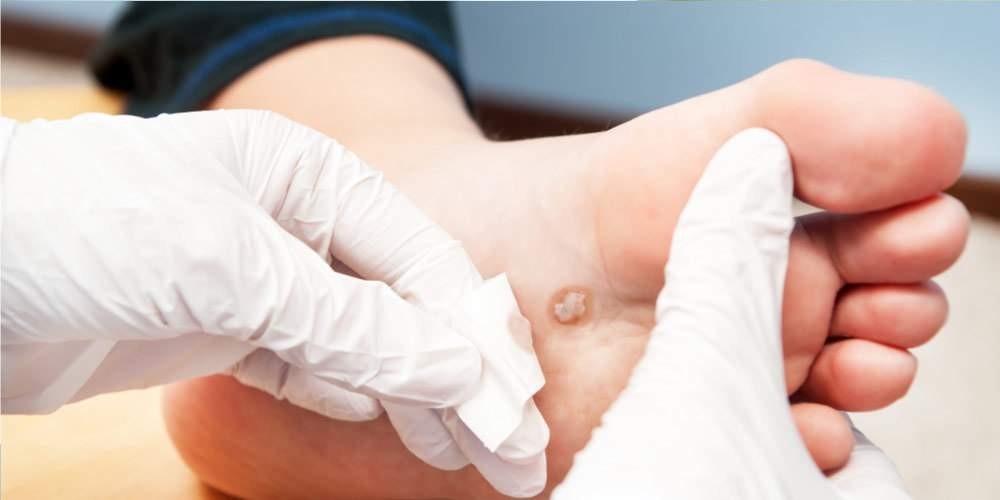
Why Proper Foot Ulcer Care is Essential for Diabetic Patients
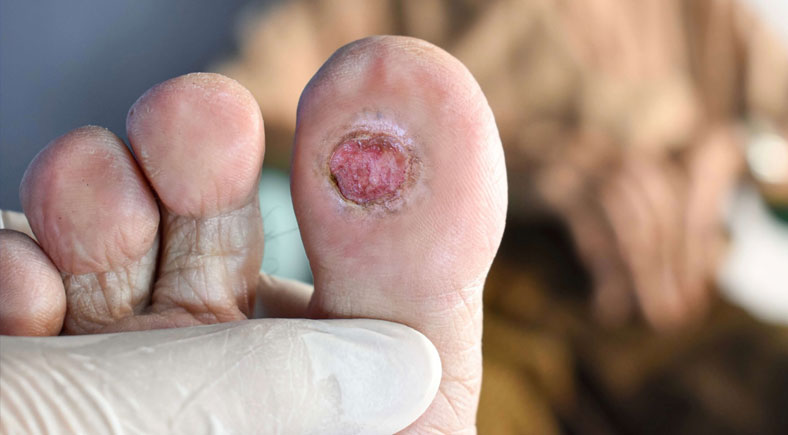
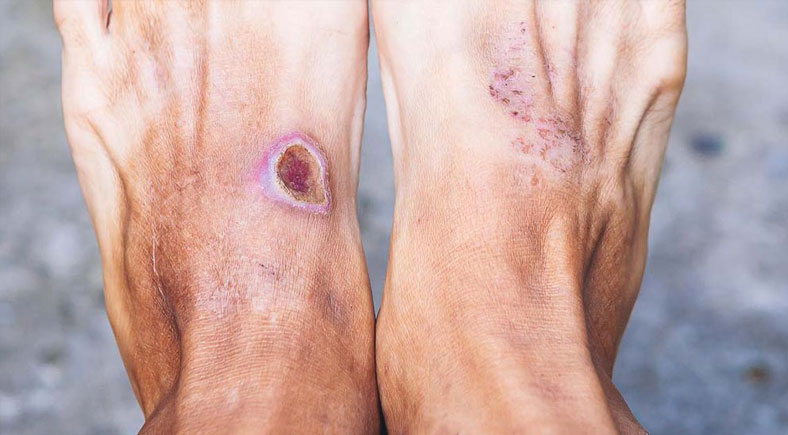
A diabetic foot ulcer is not just a minor injury, it’s a serious medical condition. The combination of reduced blood flow and nerve damage caused by diabetes makes foot ulcers harder to heal, leaving individuals at higher risk for infection. With the right care and attention, the ulcer can heal effectively, but neglecting to follow the correct diabetic foot ulcer dressing guidelines could result in complications, including infection and even amputation.
Choosing the Right Dressing: Key Diabetic Foot Ulcer Dressing Guidelines
The right dressing plays a vital role in promoting healing for diabetic foot ulcers. Choosing a dressing that suits the condition of your wound is essential for effective healing. Here are some commonly used dressing options for diabetic foot ulcers:
1. Hydrocolloid Dressings: Ideal for ulcers that don’t produce much drainage. These dressings help keep the wound moist and accelerate the healing process.
2. Foam Dressings: Perfect for ulcers with moderate drainage, foam dressings provide absorbency and cushion the wound, protecting it from further pressure.
3. Alginate Dressings: These are the best choice for ulcers that produce a lot of fluid. Alginate dressings absorb excess drainage and prevent bacterial growth, ensuring the ulcer stays clean and moist.
Always seek guidance from a healthcare provider to ensure you’re using the most suitable dressing for your ulcer.
Step-by-Step Diabetic Foot Ulcer Dressing Guidelines
Changing the dressing on a diabetic foot ulcer may seem daunting, but following these diabetic foot ulcer dressing guidelines will make it much easier:
1. Wash Your Hands Thoroughly: Before anything else, make sure your hands are clean to prevent any bacteria from entering the wound.
2. Clean the Wound: Use a saline solution or an antiseptic recommended by your doctor to gently clean the ulcer. Avoid scrubbing, as this can cause additional damage.
3. Apply the Dressing: Once the wound is clean, apply the appropriate dressing (hydrocolloid, foam, or alginate) to cover the ulcer completely. Be careful not to apply it too tightly.
4. Secure the Dressing: Use a bandage or medical tape to hold the dressing in place. Be sure it’s not too tight to avoid restricting blood flow.
5. Monitor for Signs of Infection: After the dressing is in place, check for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or unusual discharge. If any of these signs appear, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
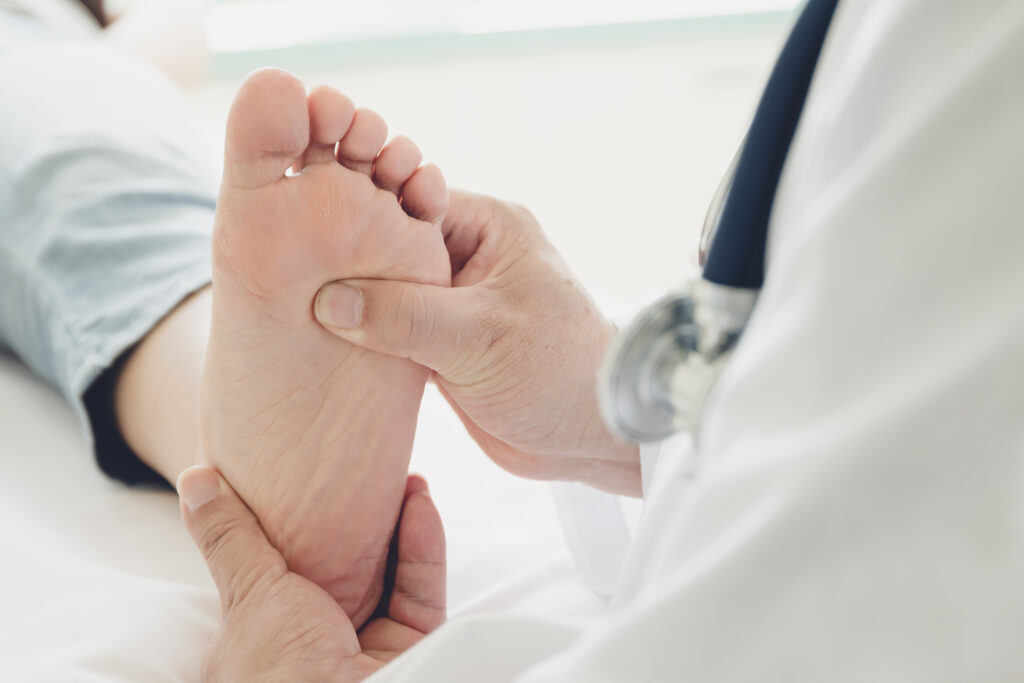
Even with the best foot and wound care at home, there are times when medical attention is necessary. If you notice any of the following, don’t hesitate to consult your healthcare provider:
- Increased redness or swelling around the ulcer.
- Foul-smelling discharge coming from the wound.
- No visible improvement in the ulcer after following dressing changes.
- Severe pain that doesn’t subside.
Chicago residents have access to expert podiatrists and wound care specialists, so seeking help is just a call away.
Why Regular Checkups Are Crucial for Foot Ulcer Care in Chicago
For Chicago residents dealing with diabetic foot ulcers, regular checkups are essential to ensure that the wound is healing properly. Podiatrists and wound care specialists can monitor your ulcer and provide professional dressing changes, helping to prevent further complications. At the Foot and Wound, we offer specialized services to help you with wound care. Learn more about our foot care services.
Conclusion: Stay Proactive with Foot Health and Follow Diabetic Foot Ulcer Dressing Guidelines
Proper care for a diabetic foot ulcer is vital to healing. By following the diabetic foot ulcer dressing guidelines outlined in this article, you can help ensure that your ulcer heals effectively and without complications. Remember, regular monitoring and the right treatment are essential for managing foot health.
If you’re in Chicago and need expert care for your diabetic foot ulcer, don’t hesitate to contact the Foot and Wound Institute today.